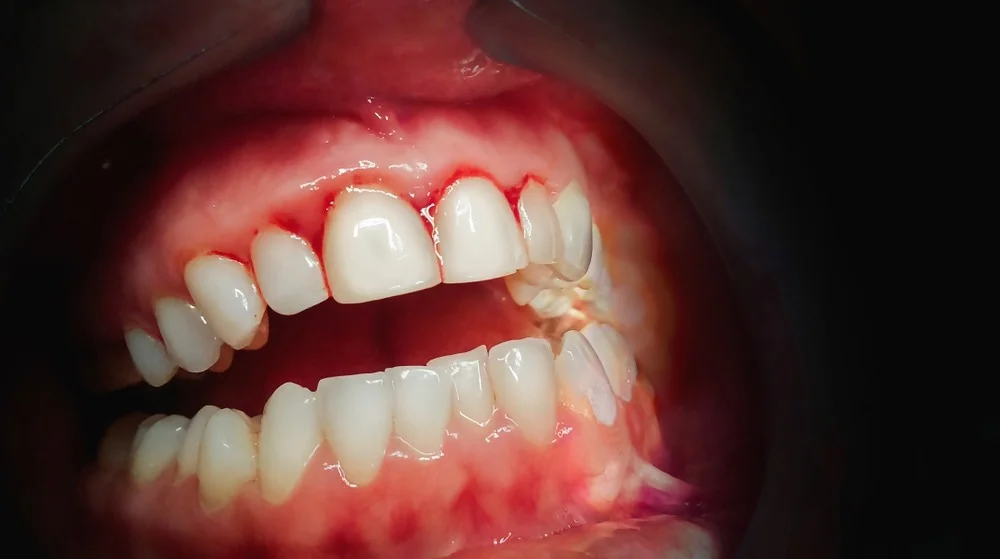
Bleeding gums can be an alarming sign of an underlying health issue, often pointing to vitamin and mineral deficiencies. The mouth is a delicate area where deficiencies in nutrients can quickly manifest, making it crucial to pay attention to any signs of discomfort or bleeding. One of the most common causes of bleeding gums is a deficiency in vital vitamins and minerals, which are necessary for maintaining the health of your teeth and gums.
In this article, we’ll explore the specific vitamins and minerals that contribute to gum health, the symptoms of deficiency, and the dental advice today on how to prevent and manage bleeding gums.
The Role of Vitamins and Minerals in Gum Health
Our gums are made of soft tissue that requires proper nutrition to stay healthy. Vitamins and minerals play key roles in the maintenance of gum tissue, supporting immune function and promoting healing. When the body lacks specific nutrients, the gums are among the first areas to show signs of damage or deficiency. Among the most important vitamins and minerals that help maintain gum health are Vitamin C, Vitamin K, Vitamin D, and calcium.
Vitamin C Deficiency and Bleeding Gums
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is crucial for the production of collagen, which is the structural protein in connective tissues. Without enough Vitamin C, the body is unable to produce collagen efficiently, leading to weakened gums and tissues. This can result in bleeding gums, as the gum tissue becomes fragile and less able to withstand everyday stress, such as chewing.
Scurvy, a disease caused by severe Vitamin C deficiency, is an extreme example of how bleeding gums can occur when this vitamin is lacking. Early signs of Vitamin C deficiency may include redness, swelling, and irritation of the gums, which can lead to bleeding when brushed or flossed. It’s important to consume adequate amounts of Vitamin C to prevent these symptoms and maintain overall gum health.
Vitamin K and Blood Clotting
Vitamin K is another essential nutrient that plays a role in blood clotting. Without enough Vitamin K, the blood may not clot properly, which can lead to excessive bleeding, including in the gums. Individuals with a Vitamin K deficiency may experience spontaneous bleeding, including frequent nosebleeds, heavy menstrual periods, and bleeding gums.
While Vitamin K deficiency is rare, it can still occur in people with certain medical conditions, those on long-term antibiotics, or those with digestive disorders that interfere with nutrient absorption. Ensuring sufficient intake of Vitamin K through foods such as leafy greens (spinach, kale), broccoli, and Brussels sprouts can help support proper clotting mechanisms and prevent bleeding gums.
The Impact of Calcium Deficiency on Gum Health
Calcium is another critical mineral when it comes to oral health. While calcium is best known for its role in maintaining strong bones and teeth, it also supports the health of the gums. Insufficient calcium levels can cause the gums to become weaker and more prone to inflammation, leading to bleeding gums.
Calcium deficiency in the body can also affect the bone structure surrounding the teeth, potentially leading to tooth mobility or even loss. Ensuring adequate calcium intake, particularly from dairy products, leafy greens, or calcium-fortified foods, is essential for preventing gum issues and maintaining strong teeth.
Vitamin D Deficiency and Gum Inflammation
Vitamin D is vital for the absorption of calcium in the body. Without adequate Vitamin D, even the best calcium-rich diet won’t be as effective. Vitamin D helps regulate the immune system and supports the inflammation response in tissues. Deficiency in this vitamin can lead to an overactive immune response, which in turn can cause inflammation and bleeding in the gums.
Studies have also linked low Vitamin D levels with an increased risk of periodontal disease, a severe form of gum disease that can lead to gum recession, tooth loss, and persistent gum bleeding. Foods rich in Vitamin D include fatty fish, fortified milk, and egg yolks. Sunlight exposure is also a natural source of Vitamin D, making it essential to get enough time outdoors for optimal gum and bone health.
Iron Deficiency and Its Effect on Gum Health
Iron is another mineral that plays a significant role in oral health, as it helps maintain healthy blood circulation and supports the immune system. Iron deficiency, or anemia, is one of the most common nutrient deficiencies in the world and can cause several oral health issues, including bleeding gums.
Anemia can weaken the body’s ability to carry oxygen in the blood, leading to poor tissue health and gum problems. Symptoms of iron deficiency anemia include pale skin, fatigue, dizziness, and bleeding gums. If you’re experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to increase iron-rich foods like red meat, spinach, lentils, and fortified cereals, or consider iron supplements if recommended by a healthcare provider.
Magnesium and Zinc for Gum Healing
Magnesium and zinc are two other minerals that contribute to healthy gums. Magnesium helps regulate calcium levels in the body, while zinc plays a crucial role in cell growth and repair. Both minerals are important for healing and maintaining healthy gum tissues. A deficiency in these minerals can slow the healing process of damaged gums and increase the risk of bleeding and infection.
Zinc has also been shown to help reduce inflammation, a major contributor to gum disease. It can be found in foods like nuts, seeds, and whole grains, and magnesium is commonly found in nuts, seeds, and green leafy vegetables. Including these foods in your diet can promote quicker healing of the gums and reduce the likelihood of bleeding.
Maintaining a Balanced Diet for Healthy Gums
The best way to prevent bleeding gums caused by deficiencies is by maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals. Regularly consuming a variety of nutrient-dense foods can ensure your body receives the essential vitamins and minerals necessary to support gum health.
Aside from specific vitamins and minerals, maintaining good overall nutrition is important for gum health. Adequate protein intake supports tissue regeneration, and staying hydrated helps maintain saliva production, which protects the gums from bacterial invasion. Limiting sugary foods and beverages is also essential, as sugar contributes to plaque buildup, which can lead to gum disease and bleeding gums.
Dental Advice Today: Prevention and Management of Bleeding Gums
If you’re experiencing bleeding gums, it’s essential to address the issue promptly. While dietary changes can play a significant role in preventing deficiencies, good oral hygiene practices are equally important. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day, using a fluoride toothpaste, and flossing daily can help keep your gums healthy and free from plaque buildup.
If bleeding gums persist despite good oral hygiene and a balanced diet, it may indicate an underlying health problem, such as a serious deficiency or a gum disease like gingivitis or periodontitis. In such cases, seeking dental advice today is critical. A dentist can perform a thorough evaluation to determine the cause of the bleeding and recommend appropriate treatment, which may include professional cleanings, a prescription for supplements, or changes in your oral care routine.
Regular dental checkups are also vital for maintaining gum health. Dentists can detect early signs of gum disease or deficiencies before they progress to more serious issues, providing a proactive approach to preventing bleeding gums.
Conclusion
Bleeding gums are a common issue, but they are often a warning sign of vitamin and mineral deficiencies. Vitamins like Vitamin C, Vitamin K, Vitamin D, and minerals such as calcium, iron, magnesium, and zinc all play critical roles in maintaining healthy gums. A deficiency in any of these nutrients can lead to gum problems, including bleeding.
By ensuring that your diet includes sufficient amounts of these essential vitamins and minerals, you can protect your gum health and prevent the discomfort of bleeding gums. Furthermore, maintaining proper oral hygiene and seeking professional dental advice today when symptoms persist are key steps to keeping your gums healthy for the long term. A combination of a nutrient-rich diet, good oral hygiene, and regular dental checkups is the best way to ensure strong, healthy gums and a confident smile.